What is a Point in Math?
When we try to show directions to a friend using pen and paper, we simply draw dots and name them to show the location of the benchmarks and the destination for our convenience. Similarly, a point in math (or, in geometry, to be specific) is a tiny dot used to show a location in space.
 Begin here
Begin here
Definition of Point in Mathematics
In math, a point is represented by a dot (.) and is used to tell exact location in space. It does not have any length, width, or height. In other words, it has no size. A point is usually named using uppercase letters.
Let’s have a look at some points — A, B, C, and D.
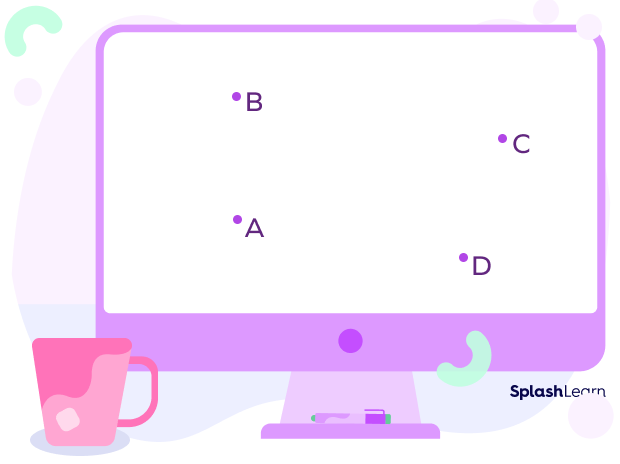
Related Worksheets
Using Points to Find a Location
Given below is a treasure hunt map. Let’s locate the position of each hidden object.
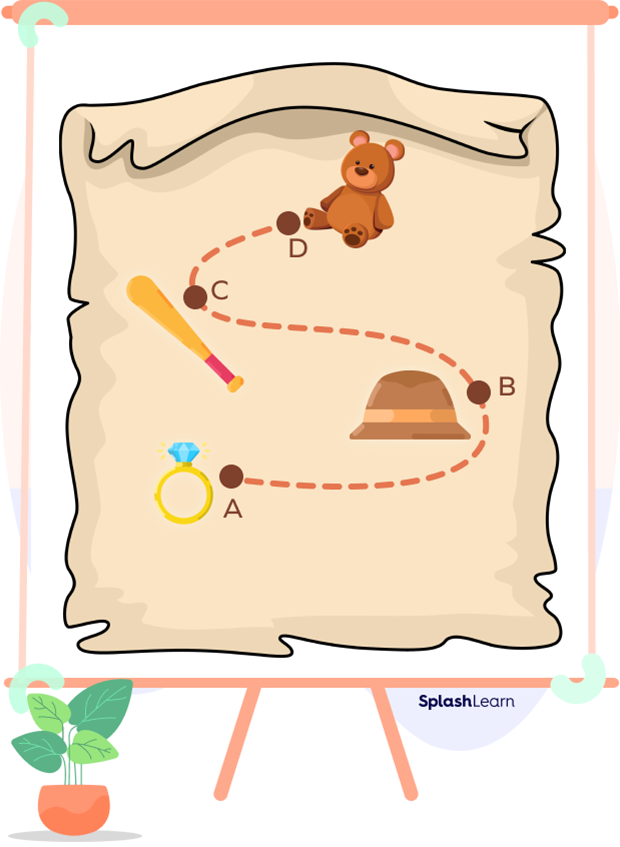
In the above image, the location of the ring is point A, the hat is at point B, the bat is point C and a dinosaur is at point D.
Point of Intersection
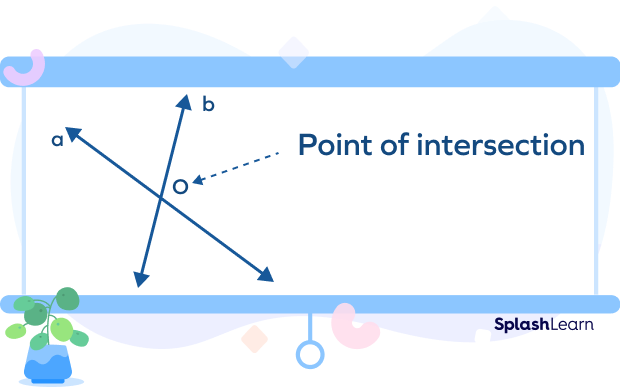
When two lines intersect each other, they cross each other at a point known as the point of intersection. In the given image, O is the point of intersection of lines a and b.
Types of Points
There are different types of points in geometry:
- Collinear Points
Collinear means something in the same line. Three or more points are said to be collinear if they lie on a single straight line.
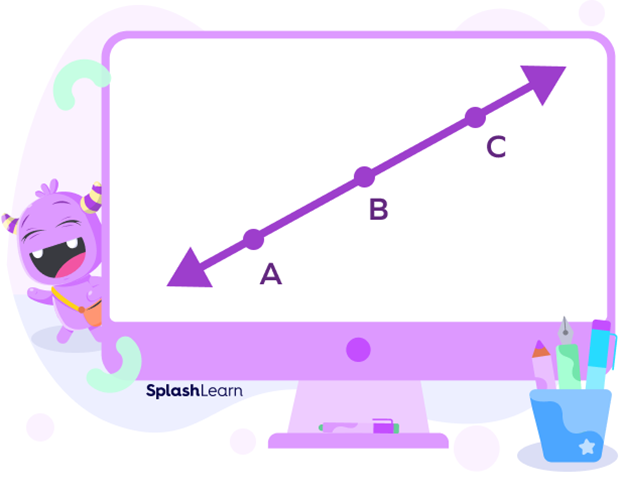
In the above figure, points A, B and C lie on the same line. So, they are collinear points.
- Non-collinear Points
Three or more points are said to be non-collinear if they do not lie on the same line. We can not draw a single straight line that passes through all these points.
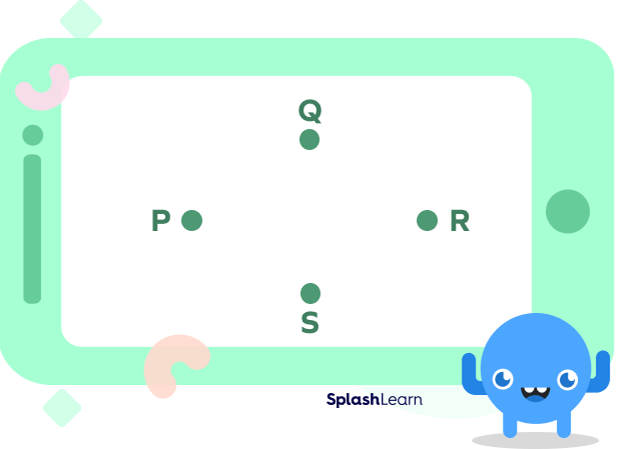
In the above figure, there is no single straight line that can pass through all these points in one go, so the points are non-collinear.
- Coplanar Points and Non-coplanar Points
Two or more points are said to be coplanar if they lie on the same plane. Two or more points are said to be non-coplanar if they do not lie on the same plane.
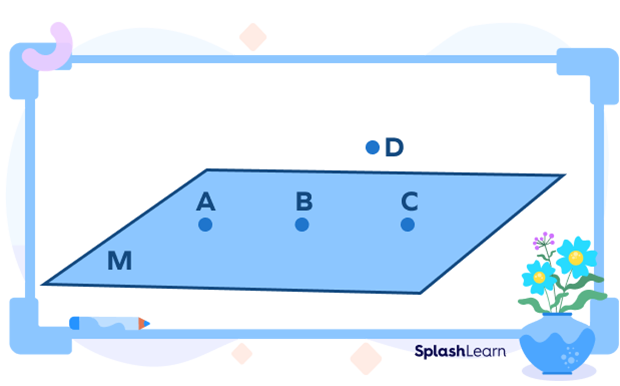
In the above figure, points A, B, and C are coplanar whereas point D is non-coplanar as it does not lie on the same plane M. In the above figure, the points A, B, and C lie on the same plane M, and hence, they are coplanar. Since the point D does not lie on the plane M, it is non-coplanar with the points A, B, and C.
- Concurrent Points
Concurrent point is the point where three or more lines intersect each other.
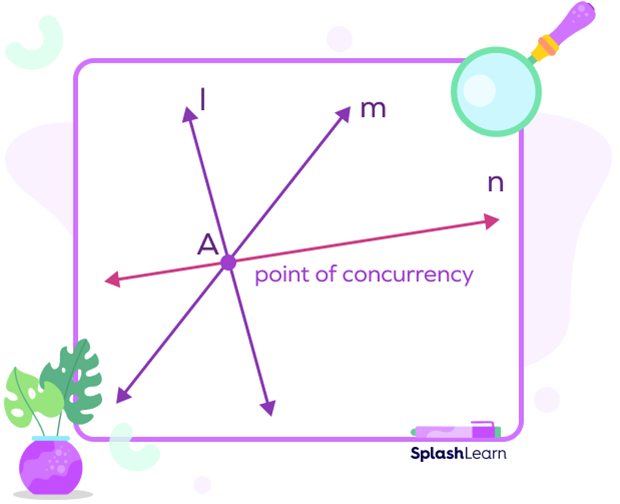
Lines l, m and n intersect each other at point O. That means A is the concurrent point or the point of concurrency.
Point in the Cartesian Plane
A point on a Cartesian plane has a unique location known as coordinates. It holds the information on how far along and how far up the point is from the origin. The coordinates of a point are expressed as an ordered pair P (x, y), where x is the horizontal distance and y is the vertical distance.
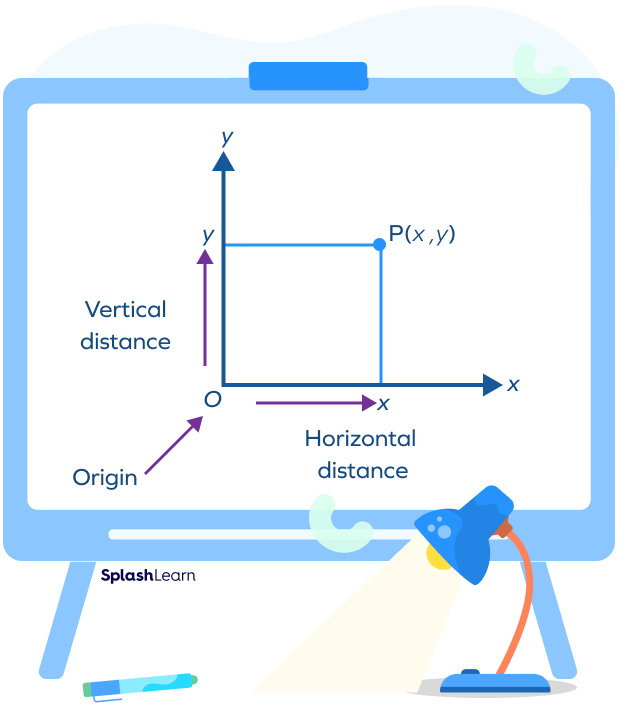
In the above figure, P is the point that is represented by (x,y).
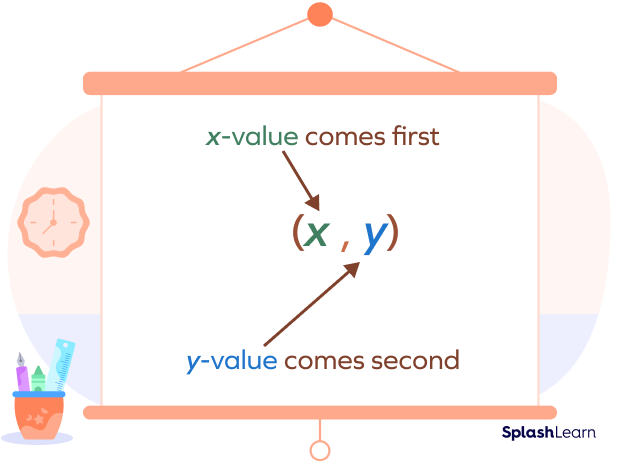
The x-value tells how the point moves either to the right or left along the x-axis.
If x-coordinate is positive, then it will be on the right side of the origin. And if the
x-coordinate is negative, then it will be on the left side of the origin.
Similarly, the y-value tells how the point moves either up or down along the y-axis.
If y-coordinate is positive, then it will be upwards from the origin. And if the y-coordinate is negative, then it will be below the origin.
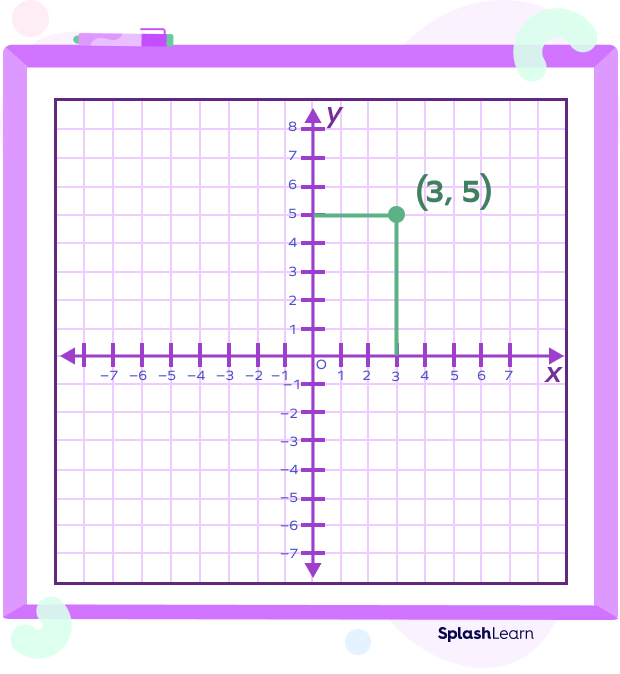
For example: A point (3, 5) is represented in the graph given below.
Solved Examples
1. What will be the ordered pair for the point for the given value of x and y coordinates if x = – 6 units and y = 4 units?
Solution: The ordered pair is written in the form (x, y) where x denotes the distance along the x-axis and y denotes the distance on the y-axis (vertical axis). So, corresponding to the given values of x and y, the point will be: (–6, 4).
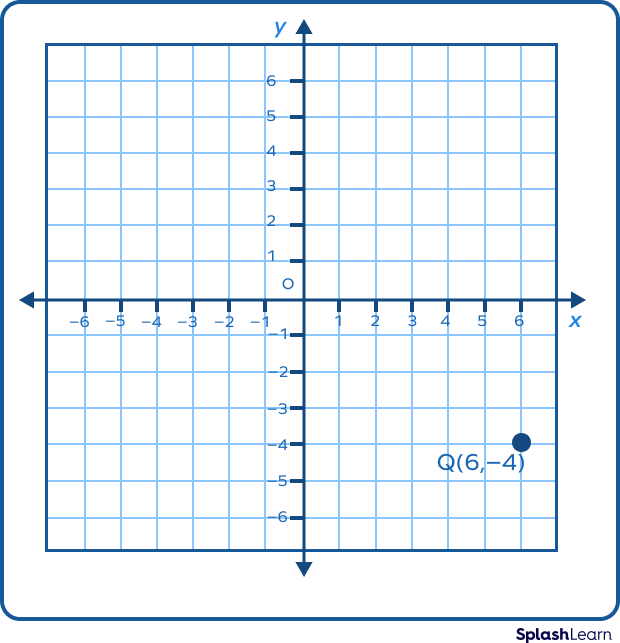
2. Plot the point (6,-4) on the graph.
Solution:
3. What is the point P called?
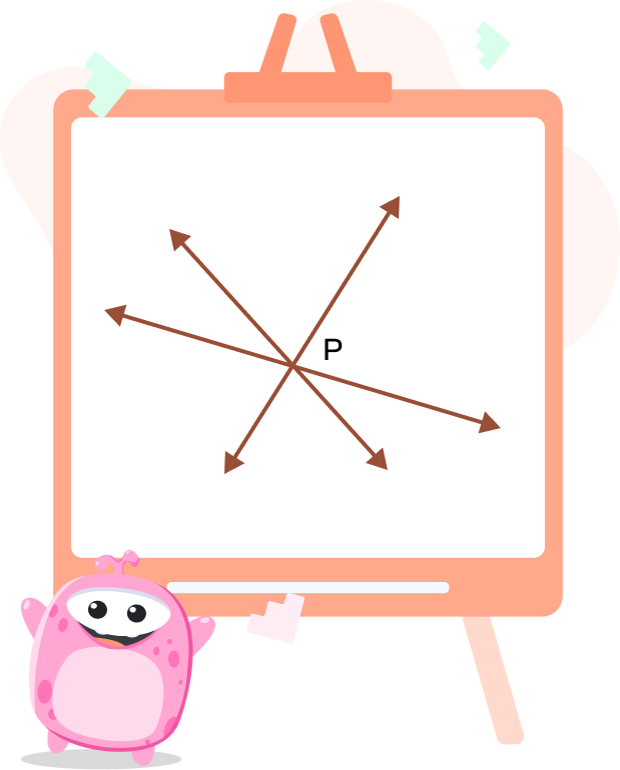
Solution: P is called the point of concurrency
Practice Problems
Point - Definition With Examples
Three or more points that lie on the same line are known as _______ points.
Collinear points are the points that lie on the same line.
If the ordered pair for the point for the given value of x and y coordinates is $(4$, $–$ $7)$, then what will be the value of y?
The ordered pair is of the form $(\text{x}, \text{y})$. So, $\text{y} = $ $–$ $7$
Which of the following does a point have?
A point does not have any length, width or thickness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a point and a line?
A point is denoted by a dot and tells the position of something. It is 0-dimensional, i.e., it has no length, no width and no thickness. On the other side, a line is formed by joining two or more collinear points. It is one-dimensional.
What is the point of origin in math?
The point of origin is the point where the two number lines, i.e., horizontal and vertical intersect each other. The point of origin is denoted by (0, 0).
What is the maximum number of points that a line can consist of?
A line consists of an infinite number of points.












